How do dolphins and whales get fresh water while living in salty seas and oceans? (7 photos)
As you know, mammals drink fresh water - their kidneys are simply not equipped to remove as much salt as is contained in the sea and ocean. A natural question arises: how do dolphins and whales cope in this case? Do they have a desalination apparatus in their body or have they adapted to salt? 
Any mammal must get enough water, otherwise it will not survive. Judge for yourself: the majority of any cell in the body consists of liquid, the basis of which is water. Where can we get it from in the seas and oceans, or have marine animals - whales, killer whales, dolphins - adapted to salt? 
The question is, of course, interesting. If you look at the life activity and structure of marine fish, it becomes clear that salt water does enter their body. However, if on average about 35 grams of salt are dissolved in one liter of sea water, in the tissues of marine fish its concentration is three times less. And all of us, tasting fish, are forced to add salt to it, although, it would seem, living in such an environment, herrings should be immediately salted. 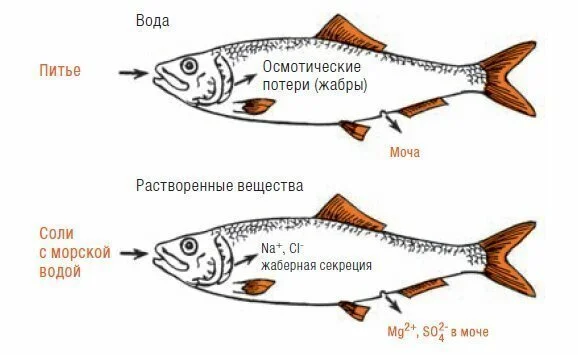
However, this does not happen. Moreover, due to strong osmotic pressure, water from the fish’s body tends to leave its body in order to minimize the difference in salt concentration in the sea and in the marine life. If not for natural mechanisms, fish would not be able to live long and would quickly die from dehydration.
However, this does not happen. Despite the scales being impenetrable to water, some of the moisture is still lost with excrement and exits through the gills during respiration. To replenish their moisture supply, fish drink sea water and “desalinize” it inside the body, removing excess salts through the intestines and, again, the gills.
Lamprey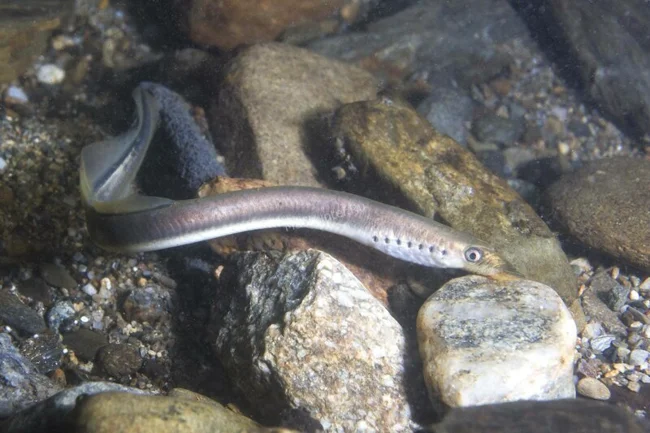 
At the same time, the amount of water that the fish is forced to drink depends on the degree of salinity. The saltier the water, the more the fish drinks and the more active its internal “desalination plant” is.
The so-called Case-Wilmer cells are responsible for this, in the membranes of which there are special proteins that carry salt ions into the external environment. In freshwater fish, the same proteins work in the opposite direction, capturing salt ions from the water. The most interesting thing is that in migratory fish, which change the sea for the river or vice versa for spawning, these proteins can switch from one mode to another. For example, during migration from sea water to fresh water, a large amount of water begins to flow through the skin of the river lamprey. To regulate its composition, the lamprey begins to secrete a lot of fresh urine, which contains almost no salts. The volume of this fluid can reach up to 45% of body weight. 
Well, we've sorted out the fish. What about mammals? Dolphins, killer whales, and whales are more complex marine inhabitants. How do they cope with excess salt in seawater? 
Cetaceans do not have such an ability to desalinate salt water, which means, firstly, they need to try in every possible way to maintain the required amount of salts and fresh water in the body. While it is quite easy to replenish the former, it is more difficult with fresh water in the seas. 
They are trying. In order not to lose moisture from the body, cetaceans do not have sweat glands, live in waters with a stable temperature (by the way, not very high) and do not drink water. And the necessary moisture is obtained from food (squid, plankton and other organisms, mostly consisting of water). Of course, along with their prey, cetaceans partially capture some sea water, but excess salt is removed from their body thanks to their complex kidneys.
In addition to food, the cetacean body receives fresh water as a product during the process of breaking down fats. Therefore, dolphins, killer whales and whales, in principle, can be called wanderers in the sea desert, creatures that live in water all their lives, but do not taste it.
