15 facts about electricity, flame, light and electromagnetic waves (16 photos)
15 questions and answers for curious people who want to increase their level of erudition. 
In case children suddenly ask a difficult question, it would be a good idea for adults to periodically refresh the knowledge acquired at school and university.
1. How does pain occur during electric shock? 
Electricity depolarizes pain receptors
Fundamentally, the work of a nerve cell is carried out in such a way that, at rest, a potential difference is maintained between the inner and outer surfaces of the cell membrane. If in some area this difference falls below a certain level, then the depolarization wave spreads to the entire surface of the cell and a nerve impulse occurs. When the body is exposed to a strong current, the electricity depolarizes and excites almost all neurons affected by it, including pain receptors.
2. Will a candle burn longer in a cold room? 
All other conditions being equal, there will be, but not much
In the flame of a candle, it is not the substance from which it is made that burns, but the vapor of this substance. Wax, paraffin or other material is successively melted by the heat emanating from the fire and rises to the active evaporation zone at the end of the wick. The colder the room, the slower the wax will melt and the candle will burn longer, but not by much.
3. What exactly is an electromagnetic wave? 
Electric and magnetic field
We believe that everything around us consists of something: cells; molecules; atoms, etc. However, electric and magnetic fields do not fit into this sequence. Which are created by electric charges, have energy and are characterized by their influence on other charges. A changing electric field generates a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field generates an electric field. This mutual generation, which is commonly called electromagnetic induction, makes it possible to separate fields from charges, as a result of which they begin to oscillate and move in space. As a result, we have an electromagnetic wave.
4. How does combustion proceed in zero gravity? 
Stops if there is no ventilation
Combustion is nothing more than the accelerated oxidation of volatile molecules with the release of a certain amount of heat. Heat gasifies flammable materials and causes air to expand. In the presence of gravity, hot air rises, taking with it combustion products, and in its place new air, enriched with oxygen, comes in, which supports the flame. In weightlessness there is no gravity, and therefore no convection; combustion products accumulate in the same place where they were formed, cutting off the combustion zone from oxygen. As a result, the flame quickly dies out and the accumulation of hot gas dissipates. However, everything described occurs only in the absence of ventilation. At manned orbital stations, to ensure the life and activities of the crew, it is always working, so fire can spread there despite weightlessness.
5. What happens if you turn on an empty microwave? 
It will fail in a few minutes
The metal walls of the microwave's inner chamber reflect the high-frequency electromagnetic waves generated by the magnetron until they reach the object being heated. In it they are absorbed, giving away their energy. But if there is no absorbent product, the energy density in the chamber increases noticeably, and microwaves from it begin to return, heating the magnetron and other electronics. As a result, after some time the equipment fails. To avoid this, some models are equipped with thermal fuses or idle start protection.
6. How many degrees of focus are there in the mirror that lights the Olympic flame?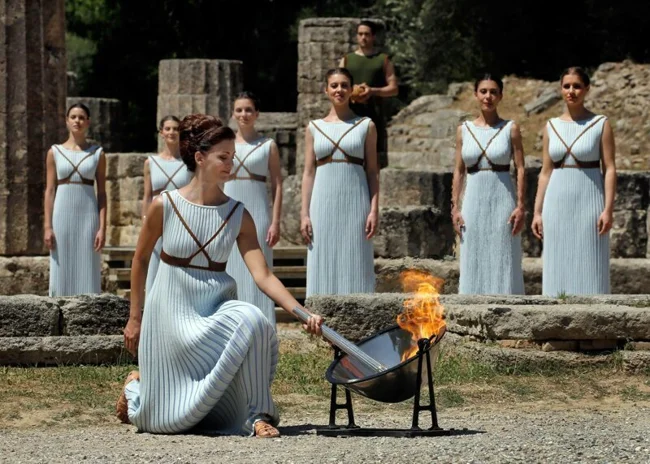 
Approximately 150°C
In order to ignite the Olympic flame, a parabolic mirror is used, which concentrates the sun's rays in the internal cavity. However, the mirror is unable to ignite the transparent gas because it does not absorb light. Therefore, a solid dark target at the end of the torch is heated. The target is usually a piece of celluloid film, which, being in the focus of the mirror, ignites at a temperature of 130 ° C, igniting the gas from a canister hidden in the torch body.
7. Where does generated but not used electricity go? 
Electricity is not generated in reserve, of course, if the battery is not used
Over a certain period, a generator produces as much electricity as is consumed by consumers. The power supply winding of the generator coil inhibits the rotation of the rotor with its magnetic field. The turbine, which is spun by hot steam or falling water, counteracts this braking. As a result, the rotor rotates stably at the same speed (otherwise the frequency of the current in the network will change). In the absence or insufficient load, the turbine does not take all the available energy from the steam or water. In such a situation, at the power plant, in order not to waste the energy and resource of the turbine, they try to reduce fuel consumption or water supply.
8. What is more effective at extinguishing fire: water or foam? 
It all depends on what, where and how it burns
Water, distributed over the burning surface, limits the access of oxygen and cools the combustion site, but quickly evaporates and the flame may remain unextinguished. Foam is better at blocking the flow of air to burning objects, but it is worse at cooling them. Wood, for example, burns through the oxidation of gases released by it at high temperatures. When water soaks into wood, it cools it more effectively than foam. When extinguishing flammable liquids, water should not be used: it can spray them, thereby increasing the combustion area. In turn, it is forbidden to extinguish live electrical installations with either water or foam, in order to avoid a short circuit. Carbon dioxide or powder fire extinguishers are used here.
9. Does the flame have a shadow?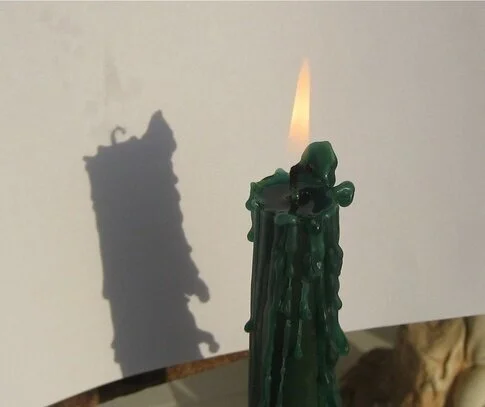 
There is a shadow, but it is faint
The flame becomes visible mainly due to hot soot particles. However, they also absorb light passing through the flame. With a relatively small flame width, this absorption is negligible and the shadow is weakly expressed. If you point a light source at a candle, a shadow on the wall will be formed mainly due to the refraction of rays in unevenly heated air. But if you light a torch and shine it through the fire along it, the shadow will become more visible, thickening towards the middle.
10. Where does lightning strike from: from the sky to the ground, or vice versa? 
She can hit both ways
Lightning is an electrical breakdown of air space. There is always a small amount of free electrons in the air. During a thunderstorm, high voltage intensively accelerates these electrons so much that when they collide with oncoming molecules, they knock out new electrons from them, forming an avalanche. The direction of movement of this flow is determined by the direction of the electric field. Typically, there is a negative charge in the clouds and a positive charge on the ground, so the electrons that form lightning move from top to bottom. However, it happens - in less than one in 20 cases - that the cloud turns out to be positively charged, and then lightning can strike from the ground to the sky. Lightning striking upward is, as a rule, many times more powerful than lightning striking downwards.
11. Why do light bulbs sometimes explode when they burn out? 
Due to the violation of the integrity of the glass flask and the entry of air into it
When the lamp is turned on, the spiral under the glass heats up to approximately 2000 °C. In the open air at this temperature, it oxidizes and burns out very quickly. And to prevent this from happening, the air is pumped out from the lamps. However, if the seal of the flask is broken, then air penetrates into it through the cracks, which, in turn, when the contacts of the electrical circuit are closed, heats up sharply and with increased pressure can destroy the flask. Following this, the spiral that finds itself in the air also burns out.
12. Where do photons go in a room after turning off the lights? 
Absorbed by wall, floor and ceiling surfaces
Photons are packets of electromagnetic waves. Separating from the source, they move at the speed of light until they reach the boundaries of the room. Then they are absorbed or reflected by them, so that with each subsequent reflection there are fewer and fewer photons. Even with a mirror surface of the walls, within a few thousand reflections, which is a few microseconds of time, all the photons will be absorbed. If the walls are painted dark, darkness will come relatively faster.
13. How does an LED lamp provide more light than a regular lamp?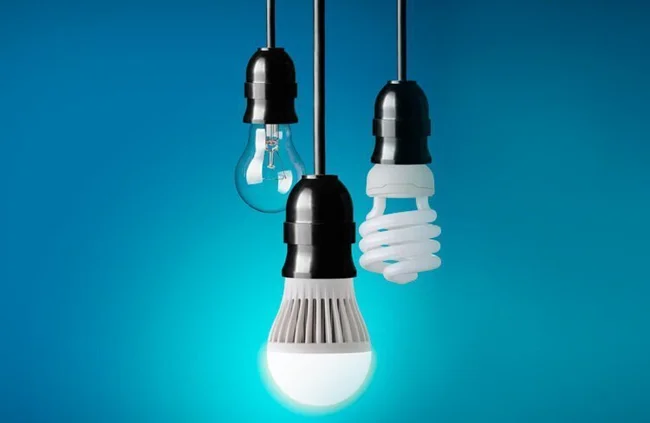 
It converts electrical energy into light more efficiently
An incandescent lamp emits most of its radiation in the infrared range. Visible light accounts for only 2–4% of electrical energy. LEDs operate on a different principle. At the point of contact of two semiconductor materials, negatively charged electrons and positively charged particles arrive towards each other, where an electron is missing. When electrons encounter particles, they fill vacancies, releasing energy in the form of light. Initially, this light is colored, and to obtain a white glow, phosphors are used, which somewhat reduce energy efficiency. However, this practically does not matter, because LED lamps are almost an order of magnitude more efficient than incandescent lamps.
14. For what reason can light not travel faster? 
This is a fundamental property of space-time, as well as the fundamental basis of our concept of the world order, if it were not so, most of the rituals of scientists over several centuries of physical and mathematical fields of science would go to the dustbin of history, like a funny but old joke. ,
The structure of space-time is such that the faster an object moves in space, the slower time flows relative to it. When the speed of light is reached, the flow of time stops. And a superluminal object would reverse the movement of time. This would make it possible to send messages, and perhaps messengers, into the past, which would inevitably lead to a violation of the principle of causality. In fundamental physics, the speed of light is taken as one, and other speeds are taken as fractions of this unit.
15. Which flashlights provide a clear circle of light? 
With a more compact light source
The structure of the light spot depends on the geometry of the lamp. The shape of the illuminated area is determined by the design of the lampshade, which limits the flow of light. And the clarity of the circle’s border depends on the compactness of the light-generating element: the smaller it is, the narrower the penumbra. For contrast of light and shadow, the flashlight must be quite bright.
