So, gluten: what is it and why is it harmful? Entire scientific studies have been devoted to this substance, and food manufacturers are tug-of-war each in their own direction: some insist on its dangers, while others say that rumors about it are fiction. Where is the truth? 
Gluten refers to a whole group of proteins found in wheat, rye, oats, and barley – grain crops. It is these proteins that provide the dough with ductility and elasticity. In addition to its natural content in grain, gluten is also found in finished products - semolina, pasta, muffins, cookies and more, where manufacturers add the component, naturally pursuing commercial gain.
Actually, the only danger of protein is its ability to cause allergies. When it enters the human digestive system, it breaks down into separate fractions. And already one of them – gliadin – is perceived by the body as a foreign substance. As a result of the immune reaction, the integrity of the intestinal mucosa is disrupted. As a result, the damaged mucosa atrophies, losing the ability to absorb normally. The body does not absorb nutrients and they turn into breakdown products, poisoning it.
Forms of gluten intolerance 
There are two forms of intolerance to such proteins:
1. Temporary. It is typical for infants during the period of complementary feeding, especially if it was started incorrectly. This is due to the fact that the child’s gastrointestinal tract is not yet fully developed. Usually the problem goes away on its own as it grows.
2. Genetic predisposition – celiac disease. This disease affects approximately 1% of the world's population. Rapid fatigue and constant weakness, frequent bloating, stomach problems, fluctuations in body weight are signs that, individually or in combination, indicate gluten intolerance. The danger of the condition is its ability to cause bone fragility, affect the thyroid gland and even provoke the appearance of neoplasms. The only possible option for preventing celiac disease is a gluten-free diet.
Illness or belief in it? 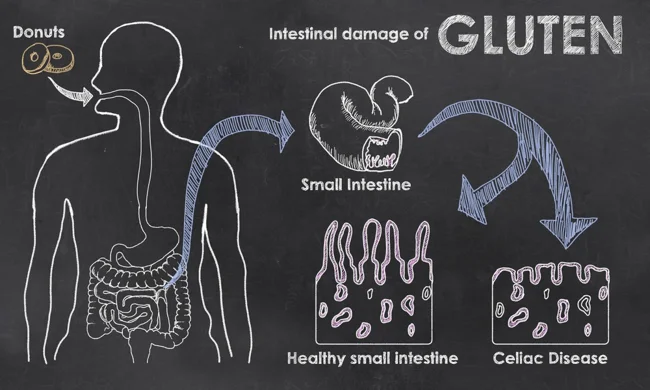
To date, none of the scientific studies conducted on gluten have confirmed all the rumors about this protein. What is the reason for the danger? After all, people have eaten bread from various grain crops throughout history. A study by the North American Celiac Disease Association disproved the theory that wheat genes are toxic. The problem is that the body is not able to fully absorb food with a colossal content of fast carbohydrates. That is, modern bread - fluffy and appetizing - contains a lot of gluten and a minimum of benefits. And the artificial additive gluten can give the appearance and feeling of a disease that actually does not exist. 
Therefore, there is no point in giving up gluten on your own in the absence of a confirmed diagnosis. Vegetable protein, although not as important for humans as animal protein, is still necessary taking into account its amino acid composition. In addition, an unfounded refusal can significantly reduce the quality of life. Since almost 1/3 of modern products contain gluten.
Gluten doesn't affect weight either. Even in the pre-gluten era, everyone knew very well that body weight would quickly increase with an unbalanced diet and uncontrolled consumption of baked goods. Refusal of gluten-containing foods for unclear purposes does not make sense. It depletes the diet and does not bring any real benefit. And if you suspect intolerance, the easiest way is to undergo an examination and proceed from its results. And there is no point in examining every store package with a magnifying glass, trying to find signs of grains of insidious gluten. After all, there are many much more interesting and useful activities in life.
0 comments
