What is special about people with negative Rh factor (7 photos)
It is known that human blood is divided into 4 groups and two Rh factors. The second group is considered the most common and 85% of the planet's population has a positive Rh factor. What about the negative? 
Back in the Renaissance, people tried to transfuse blood from one person to another for medicinal purposes. But it was only in 1818 that this procedure was successful for the first time. It took another century and a half to understand the reason why a recipient whose blood type matches the donor still dies after a transfusion. 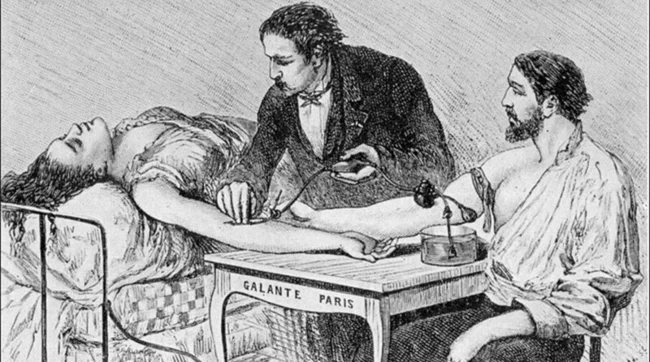
The term “Rh factor” was firmly established only in 1963 and entered into medical practice. According to the clinical studies of Drs. Landsteiner and Wiener, there is a protein and an antigen on the surface of red blood cells. But if it is not there, that is, Rh is negative and blood with antigens cannot be transfused into it, otherwise a hemolytic reaction will occur that kills the recipient. People with negative Rh are quite rare.
But apart from the difficulties with direct blood transfusion in case of emergency surgery, people with negative Rh in general do not have a problem. 
The exception is women who are pregnant from a man with positive Rh. If a child inherits the father's blood, there is a chance of an Rh conflict, which may not appear in the first pregnancy. Doctors from the Moscow Regional Research Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology explain that Rh conflict can only manifest itself if blood cells from a fetus with a positive Rh factor enter the mother’s blood. During pregnancy, the blood of the fetus and mother usually do not mix and this happens more often during childbirth. The body does not have antigens and in response to their appearance it produces antibodies that should destroy foreign cells. Modern doctors have a medicine to neutralize these consequences and save the newborn. 
But if this is the second or third birth of a woman with a negative Rh factor, and her children continue to inherit the positive blood of the father, then her body already recognizes foreign antibodies in advance and begins to destroy the fetus in the womb. But if you start timely treatment, the child will definitely be saved. It is interesting that such a situation arises at all, because the body of the expectant mother is completely rebuilt in such a way as to endure the pregnancy and save the child by any means necessary. The presence of Rh conflict always causes increased attention from doctors. 
Humanity could not do without fantastic theories of the origin of people with a negative Rh factor. At the beginning of the 21st century, the American writer Brad Steiger, who became famous for publishing popular science works about paranormal phenomena, loudly declared that people with negative Rh are the heirs of space aliens. Well, how else!
But he even substantiated his conclusions: according to Darwin’s theory, all people descended from common ancestors - monkeys. And every single primate has a positive Rh factor. And where did the mysterious negative blood come from for 15% of people on the planet and why are there still so few of its owners? 
Scientists have suggested that people with negative blood appeared on earth about 35 thousand years ago. At the same time, archaic human society began to divide into conditional nobility and aristocracy. DNA studies of the blood remains of many representatives of ancient European royal families indicate that most of them have a negative Rh factor.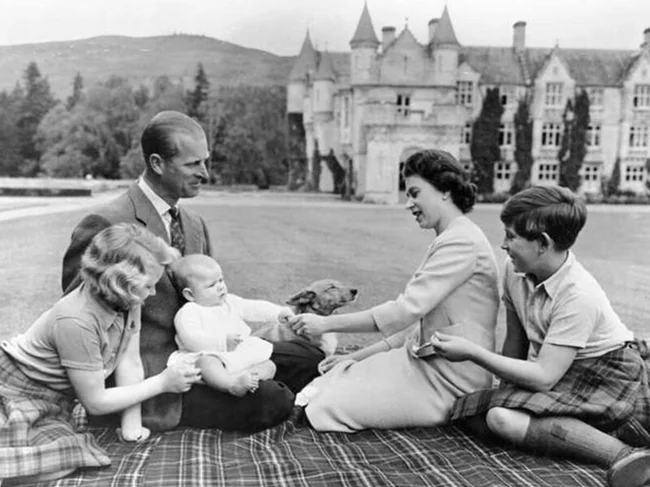 
If you look at the medical records of modern monarchs, then, for example, Elizabeth II, who is a descendant of the German Coburg-Gotha dynasty and is the great-great-granddaughter of Queen Victoria, had a negative Rh factor. Her husband, Philip Mountbatten, heir to the ancient Ottons and great-great-grandson of Tsar Nicholas I, also had Rh negative blood.
Their children were born without any Rhesus conflicts. Maybe nature initially created this prenatal hemolytic barrier to regulate noble blood in the population? And all people with a negative Rh factor are the heirs of the most ancient noble families?
